Downloading and Building Egeria Tutorial¶
Egeria is an open source project that is delivered both as source code as well as Maven Central Repository libraries.
This tutorial will guide you through the process of downloading the core Egeria source code from GitHub and building it so that you can install and run it on your local machine.
Alternatively you can also use Kubernetes to run Egeria. This uses the published builds of Egeria and does not require you to build Egeria on your machine.
Prerequisite technology for building Egeria¶
Installing Java
Installing Java¶
Java is a relatively mature object-oriented programming language that was originally designed to be able to easily run programs across a number of different computer systems.
The Egeria project itself is primarily written in Java, and therefore a Java Runtime Environment (JRE) is the most basic component needed in order to run Egeria.
You will need a Java Development Kit (JDK) installed on your machine in order to build Egeria. (A JDK will include a JRE.)
There are various JREs/JDKs available, and you may even have one pre-installed on your system. You can check
if java is already installed by running the command java -version from the command-line.
Java can be installed by:
- Downloading the OpenJDK 17 (LTS) HotSpot JVM from Adoptium.
- Running the installer that is downloaded.
Alternatively you may wish to install from your package manager such as homebrew on macOS.
Tutorial tasks¶
Downloading Egeria from GitHub website¶
Open Egeria's git repository on GitHub by clicking on this link: https://github.com/odpi/egeria. The code that is displayed is the latest version of the Egeria code and it is in a branch called main. This is the default code that will be downloaded. If you want a specific release, click on the main button to reveal a scrollable menu. Scroll down to the branches named egeria-release-{version-number} and select the release you desire.
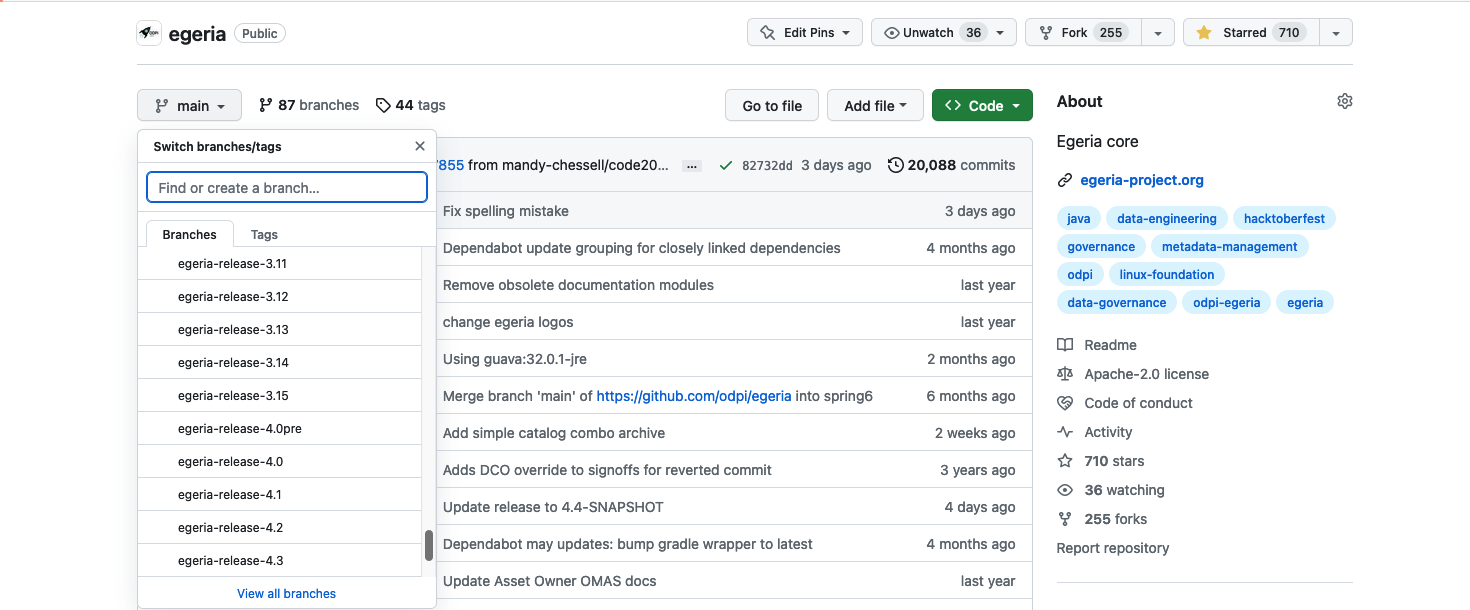
Click on the green <> Code button to reveal a menu and select Download ZIP
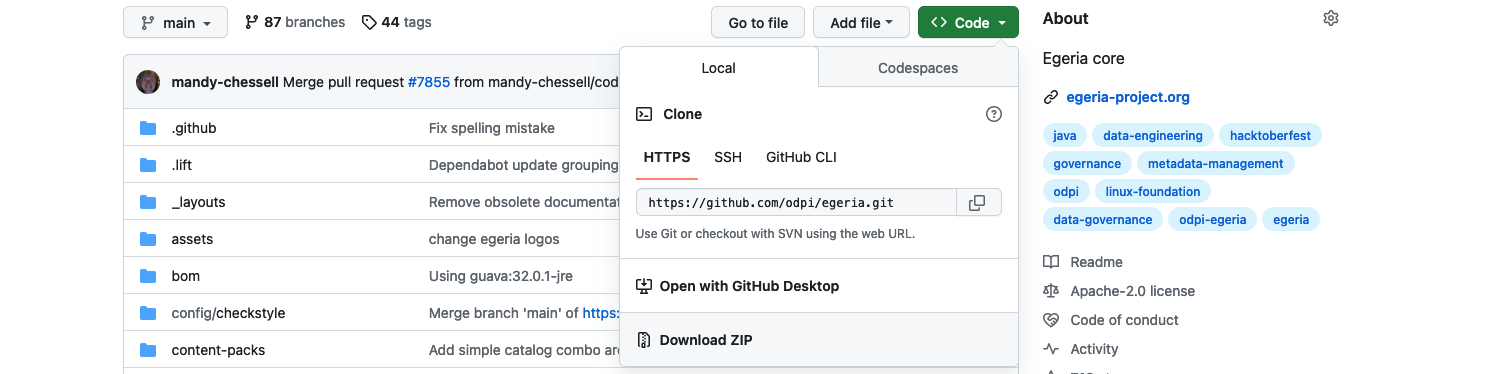
The egeria source is quite big do it may take a few minutes to download. Once it is downloaded, you can unpack the zip file into a suitable directory (folder) on your machine. The file structure will be the same as the structure shown on GitHub.
You are now ready to build the egeria source.
Building the Egeria Source¶
When you download (clone) the contents of the egeria.git repository from GitHub, a new directory is created that is named after the repository that you cloned. So the directory created when the main egeria.git repository is cloned is called egeria. This directory contains all the source and the build scripts.
Change to the egeria directory:
cd egeria
Building with Gradle (V4.0 and beyond)
The Gradle processing works through the project modules. Each module has a build.gradle file that defines the artifact, its dependencies and any special processing that the module builds. The top-level build.gradle file at the root of the repository's source code directory structure controls the overall process. It runs the build in parallel threads to speed up the process of the build, but may take many cycles of your machine's capacity. When it is running, it may be a good time for a break!
Maven repositories
This processing includes locating and downloading external libraries and dependencies, typically from an online open source repository called Maven Central and our snapshot repository on https://oss.sonatype.org, so make sure you are online when you run the build.
No gradle installation is required, as we use the 'gradle wrapper' which will automatically install gradle if needed. This reduces the setup steps, and ensure everyone runs the same version of gradle.
This is a regular incremental build, but will also run all tests and generate javadoc.
./gradlew build
The quick build skips generation of javadoc, and tests
./gradlew build -x test -x javadoc
We avoid any use of cache, and ensure a full clean build. This may be needed when you want to recheck something that has no changed sources, but needs a rebuild -- for example to review compiler warning messages (not errors)
./gradlew clean build --no-build-cache
This build option creates an OMAG Server Platform where the registered services are optional. The OMAG Server Platform loads the registered services it finds on the loader path specified with the -Dloader.path={directoryName} option of its startup command. Use this option if you want to remove the registered services that you are not using, or you would like introduce your own registered services.
./gradlew -PadminChassisOnly build
The build will typically take from seconds to 10 minutes depending on the speed of your machine and the number of projects that need to be built.
BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 4m 51s
3290 actionable tasks: 3172 executed, 118 up-to-date
Building with Maven (Before V4.0)
If building a version of Egeria prior to version 4, the maven instructions can be found below:
Prior to V4.0 Maven is used to build the following repositories:
- egeria.git - main Egeria libraries.
- egeria-samples.git - coded samples of using Egeria.
- egeria-dev-projects.git - utilities and connectors for developers to use and develop further.
The Maven processing organizes the modules into a hierarchy. Each module has a pom.xml file (called the pom file) that defines the artifact, its parent / children, dependencies and any special processing that the module builds. The top-level pom file is the pom.xml file at the root of the repository's source code directory structure.
When the Maven command is run, it passes through the hierarchy of modules multiple times. Each pass processes a particular lifecycle phase of the build (to ensure, for example, Java source files are compiled before the resulting object files are packaged into a jar file).
Maven repositories
This processing includes locating and downloading external libraries and dependencies, typically from an online open source repository called Maven Central. The directory where these external dependencies is stored locally is called .m2.
Installing Maven
Installing Maven¶
Apache Maven is a build tool at is being phased out in the Egeria project, but is still required by some repositories and the Egeria developer dojo. It is capable of code compilation, running unit tests, validating dependencies and Javadoc as well as build our distribution archive.
Where it is used, Egeria requires Maven 3.5 or higher. 3.6.x or above is recommended.
Check if Maven is installed
mvn --version
Maven can be installed by downloading the software from the Apache maven website and unpacking it into a directory that is included in your PATH. Alternatively these methods are available:
Install Maven through HomeBrew
brew install maven
Install through yum
yum install maven
Install through apt-get
apt-get install maven
On Windows, you should use Windows Subsystem for Linux Version 2 or above, install an appropriate Linux distribution, and follow the instructions for that Linux distribution.
!! cli "Rebuild a module with Maven" From the module's directory issue command:
mvn clean install
The egeria.git repository has a top-level pom file so all of the modules can be built using one mvn clean install command from the top-level egeria directory. There is also a quick build option for people just wishing to use Egeria rather than make changes - enter mvn clean install -P quick -D skipFVT
The egeria-samples.git repository does not have a top-level pom file. Each sample is built separately. When you want to build a sample, change to the sample's directory where the pom.xml file is located and issue mvn clean install.
The egeria-dev-projects.git repository has a top-level pom fileo all of the modules can be built using one mvn clean install command from the top-level egeria-dev-projects directory.
The build can take 15 minutes to over an hour depending on the repository and on the speed/load on your machine. However eventually you will see the message:
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] BUILD SUCCESS
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Total time: 54:54 min
[INFO] Finished at: 2020-01-29T09:33:17Z
[INFO] Final Memory: 171M/3510M
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
Process finished with exit code 0
Once the build is complete, the executable files you need can be found under open-metadata-distribution. Change to this directory and list the files.
cd open-metadata-distribution
ls
The directories that you see will depend on the release of Egeria. Look in the README.md for a description of the different distributions that have been built.
more README.md
Installing Egeria¶
The egeria build process creates the distribution files for Egeria in the open-metadata-distribution/omag-server-platform module. To see its contents, after a full gradle build completes, use the following cd command to change to its build/distributions directory:
cd open-metadata-distribution/omag-server-platform/build/distributions
ls
egeria-platform-{release}-distribution.tar.gz or egeria-platform-4.3-distribution.tar.gz in this example.
egeria-platform-4.3-distribution.tar.gz
Create a directory for Egeria and copy the tar file into it. The two commands shown below creates a directory in your home directory and then copies the egeria distribution file into it.
mkdir ~/egeria-install
cp egeria*-distribution.tar.gz ~/egeria-install
This next command changes to the new directory.
cd ~/egeria-install
It is now possible to unpack the tar file with the following steps.
gunzip egeria*-distribution.tar.gz
tar -xf egeria*-distribution.tar
egeria-platform-{release}-distribution.tar.gz or egeria-platform-4.3-distribution.tar.gz in this example. Change to this new directory and list its contents as shown below.
cd egeria*gz
ls
Dockerfile LICENSE NOTICE
README.md assembly dist
The Dockerfile contains the directives to build a docker image. Instructions for doing this are in the README.md file. Change to the assembly directory.
cd assembly
ls
README.md etc opt platform
platform is a directory for the OMAG Server Platform that is used to run open metadata and governance services. This is the omag-server-platform-{{release}}.jar.
ls platform
README.md data keystore.p12 logs truststore.p12
application.properties extra lib omag-server-platform-4.3.jar
platform/lib directory is where the jar files for connectors, samples and new registered services are installed. It includes the connectors that are located in the egeria.git repository.
ls platform/lib
README.md csv-file-connector-4.3.jar jdbc-integration-connector-4.3.jar
apache-atlas-rest-connector-4.3.jar data-folder-connector-4.3.jar jdbc-resource-connector-4.3.jar
atlas-integration-connector-4.3.jar discovery-service-connectors-4.3.jar kafka-integration-connector-4.3.jar
audit-log-console-connector-4.3.jar dynamic-archiver-connectors-4.3.jar kafka-open-metadata-topic-connector-4.3.jar
audit-log-event-topic-connector-4.3.jar elasticsearch-integration-connector-4.3.jar omrs-rest-repository-connector-4.3.jar
audit-log-file-connector-4.3.jar env-variable-secrets-store-connector-4.3.jar open-lineage-janus-connector-4.3.jar
audit-log-slf4j-connector-4.3.jar files-integration-connectors-4.3.jar open-metadata-archive-directory-connector-4.3.jar
avro-file-connector-4.3.jar governance-action-connectors-4.3.jar open-metadata-archive-file-connector-4.3.jar
basic-file-connector-4.3.jar governance-services-sample-4.3.jar open-metadata-security-samples-4.3.jar
cohort-registry-file-store-connector-4.3.jar graph-repository-connector-jar-with-dependencies-4.3.jar openapi-integration-connector-4.3.jar
configuration-encrypted-file-store-connector-4.3.jar inmemory-open-metadata-topic-connector-4.3.jar openlineage-integration-connectors-4.3.jar
configuration-file-store-connector-4.3.jar inmemory-repository-connector-4.3.jar spring-rest-client-connector-4.3.jar
platform/extra directory is where connectors from other repositories are added (including those that you write yourself). Copy the jar files for any additional connectors you want to use into the extra directory. The connectors available for Egeria are listed in the Connector Catalog.
The opt and etc directories contain additional content that can used with the platform. For example, the etc/reports directory contains java programs that describe different aspects of the platform.
ls etc/reports
README.md component-id-report.jar database-report.jar egeria-platform-report.jar
opt/content-packs directory contains Open Metadata Archives that provide sample open metadata content. The README.md describes their content.
ls content-packs
CloudInformationModel.json CocoGovernanceProgramArchive.json OpenConnectorsArchive.json SimpleDataCatalog.json
CocoBusinessSystemsArchive.json CocoOrganizationArchive.json OpenMetadataTypes.json SimpleEventCatalog.json
CocoClinicalTrialsTemplatesArchive.json CocoSustainabilityArchive.json README.md SimpleGovernanceCatalog.json
CocoComboArchive.json CocoTypesArchive.json SimpleAPICatalog.json
CocoGovernanceEngineDefinitionsArchive.json DataStoreConnectorTypes.json SimpleCatalog.json
/opt/sample-data directory contains sample data that is used in various labs and samples.
ls /opt/sample-data/*
opt/sample-data/README.md
opt/sample-data/data-files:
CompDir-ContactEmail.csv CompDir-ContactPhone.csv Employee-Dept.csv Location-WorkLocation.csv
CompDir-ContactList.csv EmplSAnl-EmpSalaryAnalysis.csv Employee-Employee.csv Patient-Patient.csv
opt/sample-data/database:
ibm-db2 mariadb postgresql
opt/sample-data/oak-dene-drop-foot-weekly-measurements:
week1.csv week2.csv week3.csv week4.csv week5.csv week6.csv week7.csv week8.csv week9.csv
Notice that each directory contains a README.md file that explains the content of the directory.
What next?¶
This is the end of the Downloading and Building Egeria Tutorial. You are now ready to learn about the OMAG Server Platform.
Alternatively ...
- Set up IntelliJ ready to develop connectors or clients that use Egeria or
- Run the open metadata labs to get experience with using Egeria or
- Learn about developing extensions to Egeria or
- Learn how to make a contribution to Egeria
Raise an issue or comment below